What is CASA Ratio?
CASA stands for Current Account and Savings Account, and the CASA Ratio is a key metric used to measure the proportion of a bank’s total deposits that come from these two sources. Since CASA deposits are a low-cost source of funds for banks, a higher CASA ratio indicates better financial efficiency and profitability.
Banks prefer a high CASA ratio because they pay lower interest rates on savings accounts (typically around 3-4%) and no interest on current accounts. This helps them improve their Net Interest Margin (NIM) and overall profitability.
CASA Ratio Formula
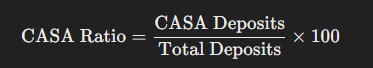
Where:
- CASA Deposits = Total money held in Current and Savings Accounts
- Total Deposits = Sum of CASA deposits, Fixed Deposits (FDs), and other term deposits
A higher CASA ratio means a bank has a greater proportion of low-cost deposits, improving its cost efficiency and lending capacity.
Example: Calculating CASA Ratio
Let’s assume Bank XYZ has:
- ₹50,000 crores in Current and Savings Accounts
- ₹1,00,000 crores in Total Deposits
Using the CASA ratio formula:
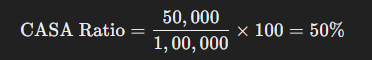
This means that 50% of Bank XYZ’s total deposits come from low-cost CASA accounts, which helps in maintaining a strong financial position.
Why is CASA Ratio Important?
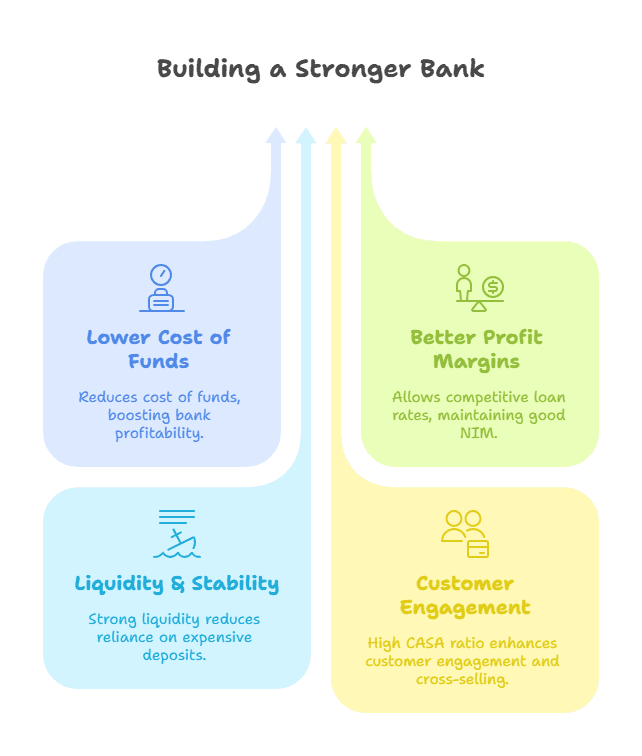
📌 Lower Cost of Funds
Banks pay little or no interest on CASA deposits, reducing their cost of funds and improving profitability.
📌 Better Profit Margins
Since CASA deposits allow banks to borrow at lower costs, they can offer loans at competitive rates while maintaining a good Net Interest Margin (NIM).
📌 Liquidity & Stability
A high CASA ratio indicates that a bank has a strong liquidity position, making it less reliant on expensive term deposits.
📌 Customer Engagement
Banks with a high CASA ratio often have a strong customer base, which can help cross-sell other banking products like loans, credit cards, and insurance.
CASA Ratio Trends in Indian Banks
- Public sector banks generally have a lower CASA ratio compared to private banks due to their focus on term deposits.
- Private banks like HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, and Kotak Mahindra Bank have a higher CASA ratio, leading to better profitability.
- Government initiatives like Jan Dhan Yojana have helped increase CASA deposits by promoting financial inclusion.
Final Thoughts
The CASA ratio is a vital indicator of a bank’s efficiency, profitability, and stability. A higher CASA ratio provides banks with a low-cost source of funds, improving their financial health and lending ability. Investors and banking professionals often monitor this metric to assess a bank’s overall strength.
💡 For investors and finance professionals, understanding the CASA ratio is crucial in evaluating a bank’s competitive edge and future growth potential! 🚀
