What is Net Interest Margin (NIM)?
Net Interest Margin (NIM) is a key profitability metric used in the banking sector. It measures the difference between the interest banks earn on loans and the interest they pay on deposits, relative to their total earning assets.
A higher NIM indicates that a bank is efficiently managing its interest income, while a lower NIM suggests higher funding costs or lower lending returns.
Formula for Net Interest Margin (NIM)
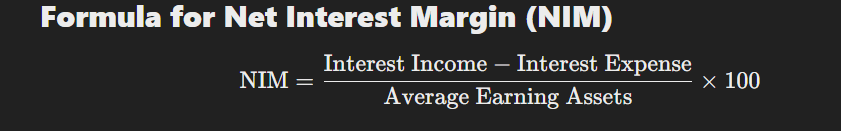
Where:
- Interest Income = Interest earned from loans, bonds, and other investments
- Interest Expense = Interest paid on customer deposits and borrowings
- Average Earning Assets = Total interest-earning assets like loans, bonds, and advances
Why is NIM Important?
NIM is a crucial metric for evaluating a bank’s profitability, risk management, and efficiency. Here’s why:
✅ Measures Profitability
A higher NIM means a bank is earning more from its loans compared to what it pays on deposits, leading to higher profits.
✅ Indicates Financial Stability
Banks with a healthy NIM can withstand economic downturns better since they generate consistent income from their core business—lending.
✅ Helps Compare Banks
Investors and analysts use NIM to compare the efficiency of different banks. A declining NIM could signal increasing costs or weaker loan demand.
Ideal NIM Range for Indian Banks
In India, the ideal Net Interest Margin (NIM) range varies between:
🔹 Public Sector Banks (PSBs): 2.5% – 3.5%
🔹 Private Sector Banks: 3.5% – 4.5%
🔹 NBFCs & Small Finance Banks: 5%+ (due to higher lending rates)
Public sector banks generally have lower NIMs due to their focus on priority sector lending and government schemes. Private banks, on the other hand, manage risk better and operate with higher efficiency, leading to better margins.
How Can Banks Improve Their NIM?
To increase Net Interest Margin, banks can:
✔ Increase lending rates while remaining competitive
✔ Reduce deposit rates to lower funding costs
✔ Optimize asset allocation toward high-yield loans
✔ Expand fee-based income to supplement interest revenue
Conclusion
Net Interest Margin (NIM) is a key financial metric that reflects a bank’s ability to manage its lending and borrowing efficiently. A higher NIM means better profitability, but it must be balanced with sustainable growth.
For Indian banks, a NIM of 3% – 4% is generally healthy, with private banks often outperforming public banks. Investors should monitor NIM trends to gauge a bank’s financial health before making investment decisions.
💡 Want to learn more about banking profitability metrics? Stay tuned for more financial insights! 🚀
