What is Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR)?
The Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR) is a vital financial metric used by banks to assess the quality of their loan portfolios. PCR measures the extent to which a bank has made provisions to cover its non-performing assets (NPAs). Essentially, it indicates how well a bank can absorb losses from bad loans, ensuring better financial stability.
A higher PCR signifies that the bank is well-prepared for potential losses, which in turn reflects prudent risk management and a healthier balance sheet.
How is PCR Calculated?
The formula for calculating the Provision Coverage Ratio is:

Where:
- Provisions for NPAs: Funds set aside by the bank to cover expected losses from non-performing loans.
- Gross NPAs: The total amount of loans that are classified as non-performing before any provisions are made.
Why is PCR Important?
📌 Indicator of Asset Quality and Risk Management
PCR provides insight into a bank’s ability to manage credit risk. A higher PCR means the bank has reserved more funds to cover potential losses, reflecting strong risk management practices.
📌 Impact on Profitability and Stability
Adequate provisioning, as reflected by a robust PCR, protects a bank’s earnings by cushioning the impact of bad loans. This not only supports profitability but also enhances the overall stability of the financial institution.
📌 Investor Confidence
Investors and analysts closely monitor PCR as it offers a clear picture of a bank’s financial health. A well-maintained PCR can boost investor confidence, signaling that the bank is proactive in managing its asset quality.
Example: Calculating the PCR
Imagine Bank XYZ has the following data:
- Gross NPAs: ₹800 crores
- Provisions for NPAs: ₹400 crores
Using the PCR formula:
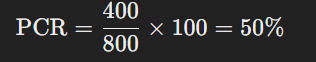
This means that Bank XYZ has covered 50% of its gross NPAs with provisions. A 50% PCR indicates a moderate level of provisioning, and stakeholders might compare this value with industry benchmarks to assess risk management effectiveness.
PCR Trends in Indian Banks
In the Indian banking sector, PCR values can vary across different types of banks:
- Public Sector Banks (PSBs): Often maintain higher PCRs due to legacy NPAs and regulatory expectations.
- Private Banks: Generally target a balanced PCR reflecting efficient provisioning while maintaining profitability.
- NBFCs & Small Finance Banks: Their PCRs can vary significantly based on their unique risk profiles and loan portfolios.
Final Thoughts
The Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR) is a key metric that highlights a bank’s preparedness for potential credit losses. By analyzing PCR, investors and analysts can gauge how well a bank is managing its non-performing assets and mitigating risks. In the dynamic landscape of Indian banking, a strong PCR is often seen as a sign of sound risk management and financial health.
💡 Stay informed about essential banking metrics like PCR to make smarter investment decisions and better understand the financial stability of banks! 🚀
